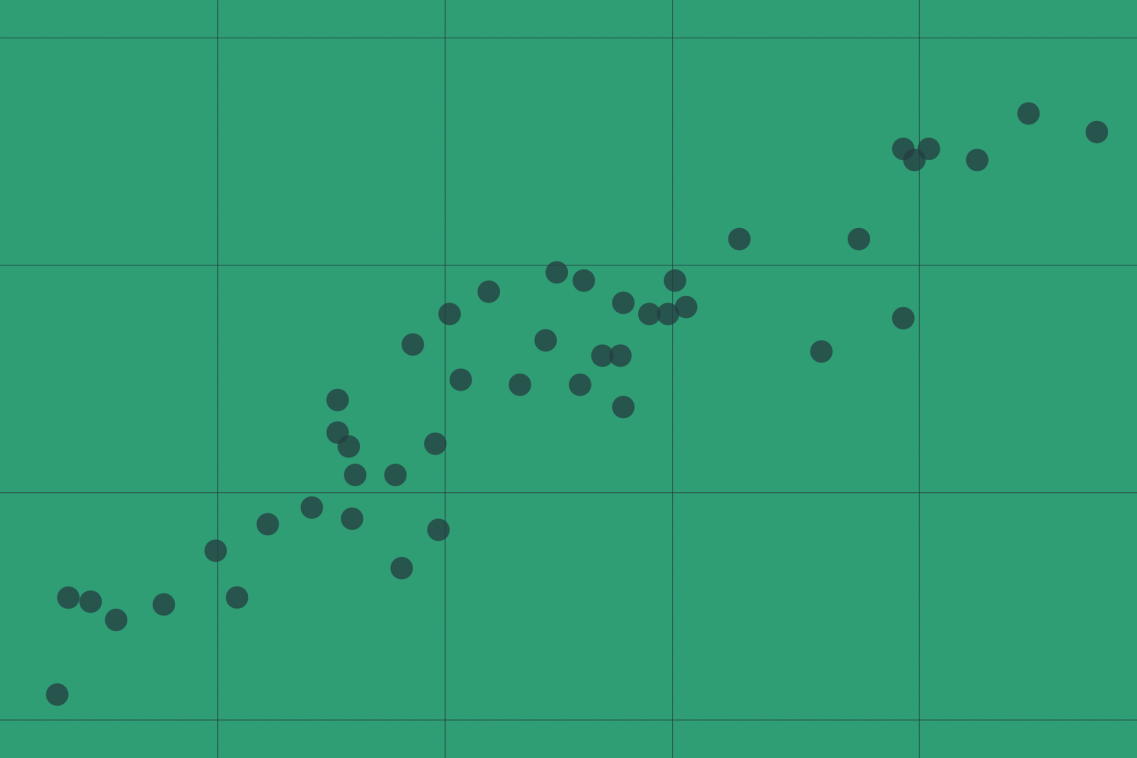
Comment
Over 50 countries and localities, including the UK, have recently introduced taxes on soft drinks. In new IFS research funded by the National Institute of Health Research under the Department for Health’s Obesity Policy Research Unit, we survey the evidence on the effects of soft drink taxes on prices and purchases in 27 studies covering 11 jurisdictions (Berkeley, Boulder, Catalonia, Chile, France, Maine, Mexico, Ohio, Philadelphia, Portugal and Washington).